Interesting piece of technology being put together by AMD in regards to their next generation Radeon 300-series graphic cards, the technology on topic is HDM ,better know as HBM High Bandwidth Memory. This technology will have the GPU operate differently by having access to memory upside down. HBM technology will impose changes on how memory within your graphic card will operate. Lets explore in depth.
Current GPUs ( graphic processing units) that includes the likes of AMD Radeon 290X and NVIDIA GeForce GTX 980, two of the top graphic cards in the business uses GDDR5 , but there is a slight issue with that technology.
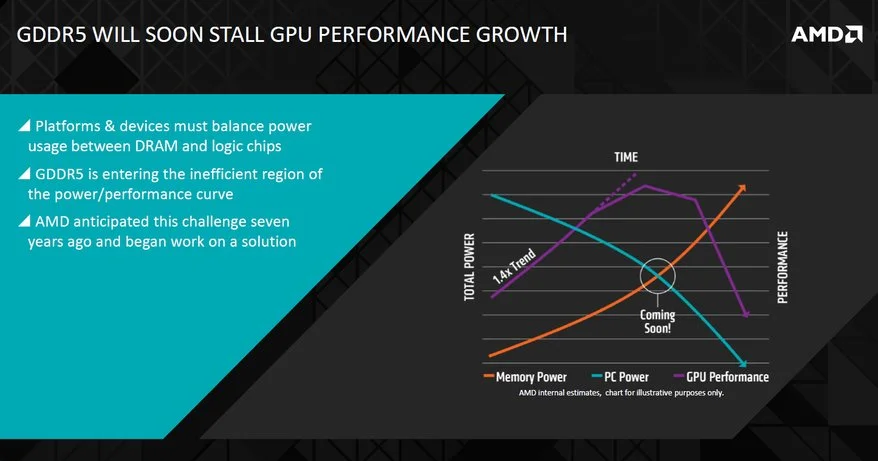
According to AMD,they state that there will soon be a stall in GPU growth , GDDR5 technology is entering an inefficient power-performance curve. In the past,AMD solve the power-performance issue by simply shrinking the integrated circuit chips. This method is usually achieved on processors not DRAM.
Theoretically according to AMD you can make GDDR5 operate much faster,but doing so would require a lot of power.
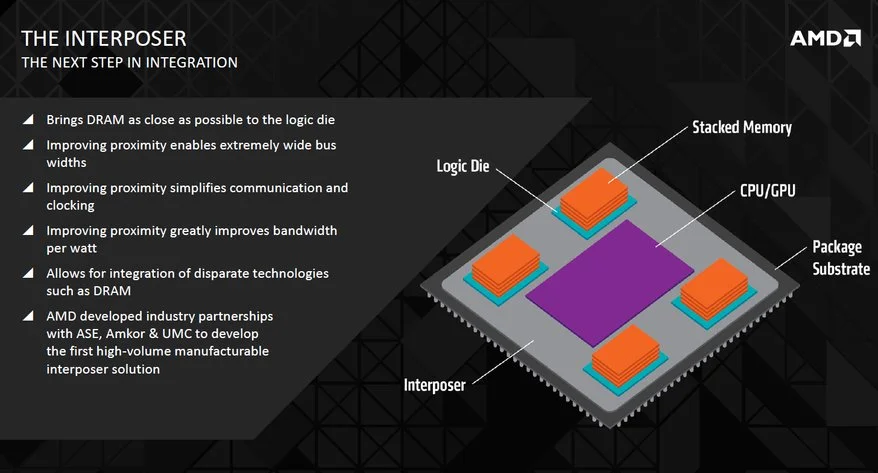
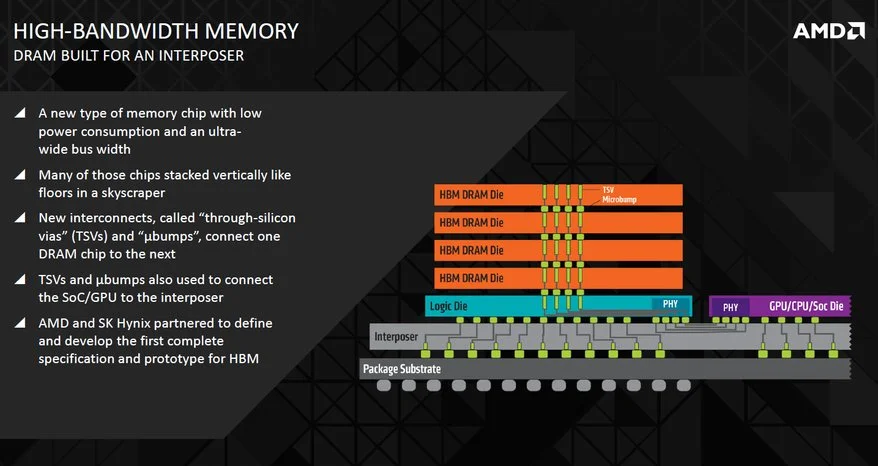
To solve this issues,AMD is implementing a method call interposer. this would bring the DRAM much closer to the logic die. this is the next generation of integration that will bring components much closer, at the same time will create much wider bus lanes. This will improve overall bandwidth throughput,overall speed will be of greater emphasis than having an large abundance of RAM. Speaking of RAM, this new technology will have stacks of RAM that will equate to about 1GB. AMD next GPU in theory will have 4GB of high bandwidth memory,which will add up to four stacks.
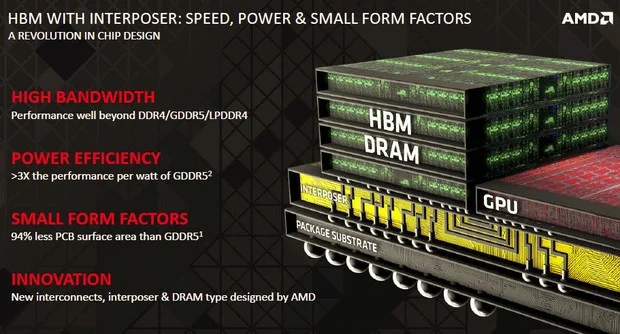
There are unlimited benefits in using the interposer method, besides having an high amount of bandwidth, the surface area on the chip will be less condense and will use 50 percent less power.
AMD wants this technology to just not cover GPU's, but they want to also apply this technology to APU's,consumer applications and enterprise solutions. This will add 3 x the watt performance and 94% less PCB surface.
Are you ready for the next generation graphic card technology?